
An example of how you can create entities in Kubernetes using AWS Lambda.
The function will be in Python3, so we will use Kubernetes Python Client
More usage examples can be found here.
Since AWS Lambda does not support this package, we will pack the "kubernetes" and "boto3" modules in our function.
"boto3" is needed to access AWS SSM, where kubeconfig will be stored
Preparation
Create a directory for the lambda and go to it:
mkdir lambda cd lambda
Next you will need "virtualenv", if it is not there, you can install it using "pip3":
pip3 install virtualenv
Create a virtual environment and activate it:
python3 -m virtualenv . source bin/activate
And install the necessary modules:
pip3 install kubernetes pip3 install boto3
Next, we only need the contents of this directory:
$VIRTUAL_ENV/lib/python3.7/site-packages
"python3.7" – replace with your version of Python
It will be more convenient to look at the environment path and copy the contents to a separately created directory, no longer in a virtual environment:
echo $VIRTUAL_ENV/lib/python3.7/site-packages /private/tmp/lambda/lib/python3.7/site-packages
Let’s create a directory for lambda, which we will already directly download and copy our modules:
mkdir ~/lambda_upload cp -R /private/tmp/lambda/lib/python3.7/site-packages/. ~/lambda_upload/
SSM Parameter Store
In the AWS console, go to "Systems Manager" -> "Parameter Store"
And create a parameter with the type "SecureString" and copy the contents of the "kubeconfig" file as the value. If this is an EKS, first create a service account so that it does not require AWS authorization, as in the example below:
Kubeconfig with AWS authorization:
...
user:
exec:
apiVersion: client.authentication.k8s.io/v1alpha1
args:
- --region
- eu-central-1
- eks
- get-token
- --cluster-name
- artem-services-stage-eks
command: aws
Function
Now in the directory "~/lambda_upload" create a file called "lambda_function.py" and paste the following text into it:
lambda_function.py:
import os
import time
import random
import string
import boto3
from kubernetes import config
from kubernetes.client import Configuration
from kubernetes.client.api import core_v1_api
from kubernetes.client.rest import ApiException
from kubernetes.stream import stream
# Get Kubeconfig from SSM
def get_kube_config():
awsRegion = os.environ['AWS_REGION']
ssmParameter = os.environ['SSM']
ssm = boto3.client('ssm', region_name=awsRegion)
parameter = ssm.get_parameter(Name=ssmParameter, WithDecryption=True)
kubeconfig = open( '/tmp/kubeconfig.yaml', 'w' )
kubeconfig.write(parameter['Parameter']['Value'])
kubeconfig.close()
# Generate random string for unique name of Pod
def randomString(stringLength=8):
letters = string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits
return ''.join(random.choice(letters) for i in range(stringLength))
def exec_commands(api_instance):
name = "busybox-" + randomString()
namespace = "default"
resp = None
print("Creating pod...")
pod_manifest = {
'apiVersion': 'v1',
'kind': 'Pod',
'metadata': {
'name': name
},
'spec': {
'containers': [{
'image': 'busybox',
'name': 'busybox',
"args": [
"/bin/sh",
"-c",
"while true;do date;sleep 5; done"
]
}]
}
}
resp = api_instance.create_namespaced_pod(body=pod_manifest, namespace=namespace)
while True:
resp = api_instance.read_namespaced_pod(name=name, namespace=namespace)
if resp.status.phase == 'Pending' or resp.status.phase == 'Running':
print("Done. Pod " + name + " was created.")
break
time.sleep(1)
def main(event, context):
get_kube_config()
config.load_kube_config(config_file="/tmp/kubeconfig.yaml")
c = Configuration()
c.assert_hostname = False
Configuration.set_default(c)
core_v1 = core_v1_api.CoreV1Api()
exec_commands(core_v1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Now all the contents of the directory can be packed into a "zip" archive and loaded into the Lambda function.
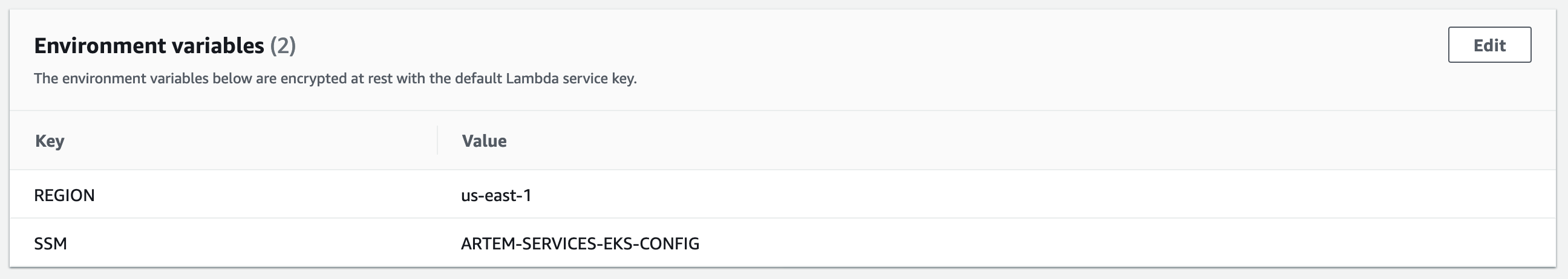
In a variable environment, create 2 variables in which indicate your AWS Region and the name of the SSM Parameter Store that you created earlier.
Lambda functions require read permissions from SSM, so attach the following policy to the role that Lambda uses:
arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonSSMReadOnlyAccess
After starting the function, it will create a pod named "busybox-" + the generated string of 8 characters. There is no pod status check, since this script is planned to be used for EKS Fargate, so as not to wait 1-2 minutes until the Fargate instance will running, so in any of the conditions, "Pending" or "Running", we consider that the pod was successful created.