
See the list of AMI Linux add-ons:
sudo amazon-linux-extras list
Install from php7.2 extensions:
sudo amazon-linux-extras install php7.2

See the list of AMI Linux add-ons:
sudo amazon-linux-extras list
Install from php7.2 extensions:
sudo amazon-linux-extras install php7.2
By default, CentOS uses MariaDB, to install MySQL, you need to add a repository:
sudo rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm
See the list of repositories:
sudo yum repolist
Install:
sudo yum install mysql-community-server
Download the latest version for 64-bit architecture:
wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_x86_64.rpm
Install:
sudo yum install ./google-chrome-stable_current_*.rpm
Run in console:
google-chrome &
When trying to set a password for the mysql user, the following error occurs:
ERROR 1819 (HY000): Your password does not satisfy the current policy requirements
This error appears if your password does not meet the following requirements, for "validate_password.policy" in "MEDIUM" mode it is:
1. Set a password that meets the security requirements for passwords.
2. Or lower the password security requirement level:
If the second option suits you, then log in to mysql and look at the current value:
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'validate_password%'; +--------------------------------------+--------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------------------+--------+ | validate_password.check_user_name | ON | | validate_password.dictionary_file | | | validate_password.length | 8 | | validate_password.mixed_case_count | 1 | | validate_password.number_count | 1 | | validate_password.policy | MEDIUM | | validate_password.special_char_count | 1 | +--------------------------------------+--------+ 7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
And lower the level:
SET GLOBAL validate_password.policy=LOW;
We stop the mysqld service and start it with the following keys:
sudo mysqld --skip-grant-tables --user=mysql &
Log in without a password:
mysql -u root
And run:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES; ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'YOUR_NEW_ROOT_PASSWORD'; \q;
Now the mysqld service running in the background needs to be stopped. We look at the process ID:
sudo ps aux | grep mysql
Kill the process:
sudo kill 12345
And start the mysqld service:
sudo systemctl start mysqld

Example manifest for creating a configmap, deployment and service for RabbitMQ
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: rabbitmq-config
namespace: staging
labels:
app: rabbitmq
data:
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER: "user"
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS: "password"
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_VHOST: "vhost"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: rabbitmq
namespace: staging
labels:
app: rabbitmq-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: rabbitmq-app
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
progressDeadlineSeconds: 300
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: rabbitmq-app
spec:
containers:
- image: rabbitmq:3
name: rabbitmq
imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: rabbitmq-config
ports:
- containerPort: 5672
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/rabbitmq
subPath: data/rabbitmq
name: persistent-storage
volumes:
- name: persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: persistent-storage
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: rabbitmq-svc
namespace: staging
spec:
ports:
- port: 5672
targetPort: 5672
selector:
app: rabbitmq-app

Manifest example for creating deployment and service for PostgreSQL
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: postgres
namespace: staging
labels:
app: postgres-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: postgres-app
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
progressDeadlineSeconds: 300
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: postgres-app
spec:
containers:
- image: postgres:11
name: postgres
imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
ports:
- containerPort: 5432
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data
subPath: data/postgres/data
name: persistent-storage
volumes:
- name: persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: persistent-storage
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: postgres-svc
namespace: staging
spec:
ports:
- port: 5432
targetPort: 5432
selector:
app: postgres-app

apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: persistent-storage
namespace: staging
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadOnlyMany
volumeMode: Filesystem
resources:
requests:
storage: 30Gi
storageClassName: standard
Create PVC:
kubectl create -f pvc.yml
Check:
kubectl get pvc -n staging NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE persistent-storage Bound pvc-bd856312-9be4-11e9-bb1d-42010a9c01f3 30Gi ROX standard 17s

As it turned out, CodeBuild does not have a built-in incremental variable for the build number, as in Jenkins, for example.

The solution was found on medium.com
To add the build number you will need the following services:
Go to the service AWS Systems Manager –> Parameter Store
Create a parameter named "/build-number/artem-test"
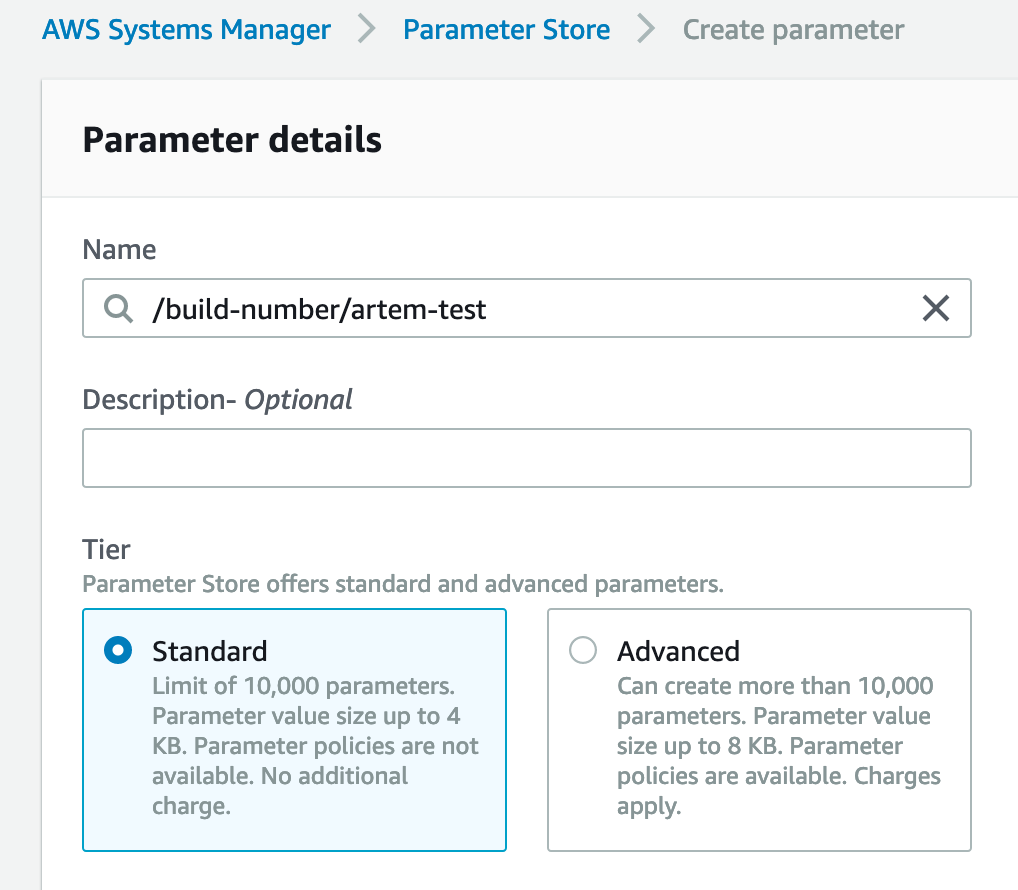
Set the parameters:
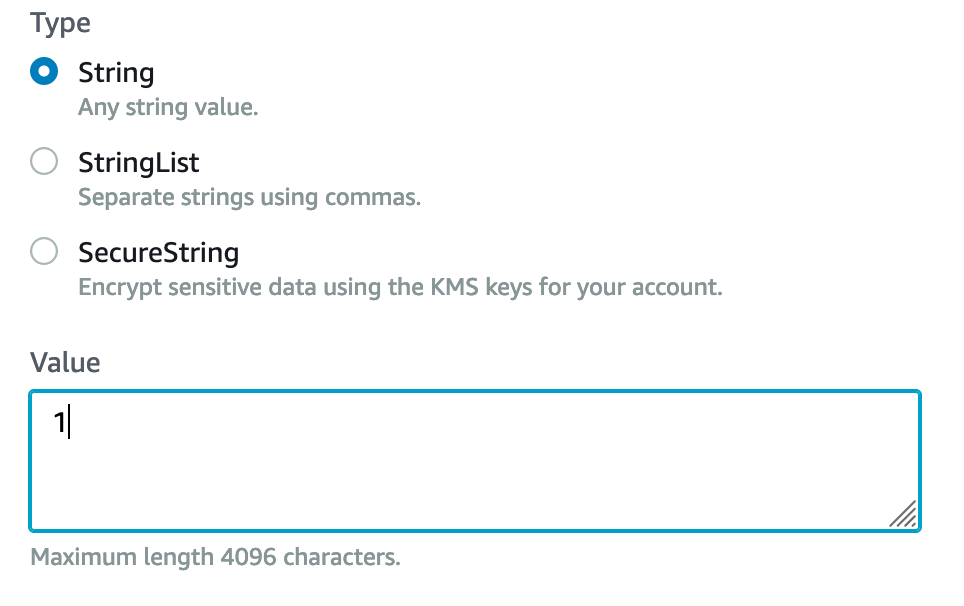
Save our "Parameter store"
Go to AIM -> Policy
Create a new Policy with the name "codebuild-buildnumber-ssm" for the "CodeBild" project with the following contents:
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ssm:GetParameter",
"ssm:GetParameters"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:ssm:us-east-1:XXXXXXXXXXXX:parameter/build-number/*"
}
]
XXXXXXXXXXXX – replace with your AWS ID. Also check your region.
Go to AIM -> Roles and find the role of CodeBuild for our project and make it "Attach" created by the Policy.
Continue reading "AWS – CodeBuild: Add an incremental build number"

In this example, we will consider creating a repository in CodeCommit and building a simple Docker image using CodeBuild and launching it in ECR.
Create a repository in CodeCommit. My repository name is "artem-test"
In order to work with the repository, make sure that your user has an SSH key loaded. If it is already loaded, look at its ID, it will be needed.
We clone our repository:
git clone ssh://[email protected]/v1/repos/artem-test
Do not forget to change the region in which the repository is created.
Add to it for the test an example of a simple Dockerfile.
FROM php:7.1-apache-jessie
RUN apt update && \
apt install curl net-tools && \
apt-get clean
CMD ["apache2-foreground"]
For the build we will use: buildspec.yml
version: 0.2
env:
variables:
AWS_ACCOUNT_ID: "XXXXXXXXXXXX"
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: "us-east-1"
IMAGE_REPO_NAME: "artem-test"
IMAGE_TAG: "latest"
phases:
install:
runtime-versions:
docker: 18
pre_build:
commands:
- echo Logging in to Amazon ECR...
- $(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email --region $AWS_DEFAULT_REGION)
build:
commands:
- echo Build started on `date`
- echo Building the Docker image...
- docker build -t $IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG .
- docker tag $IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION.amazonaws.com/$IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG
post_build:
commands:
- echo Build completed on `date`
- echo Pushing the Docker image...
- docker push $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID.dkr.ecr.$AWS_DEFAULT_REGION.amazonaws.com/$IMAGE_REPO_NAME:$IMAGE_TAG
Send local changes to the server:
git add . git commit -am "git init" git push
Create a project in CodeBuild, specifying as a source repository in CodeCommit.
We give for CodeBuild rights in ECR
Open IAM -> CodeBuild
Looking for "codebuild-artem-test-service-role"
And we add the following Policy to this role:
AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryPowerUser
To display the build logs, go to the "CloudWatch" service and create a group. You can also create an S3 Bucket to store log archives.
You can try to build an image in CodeBuild.